 |
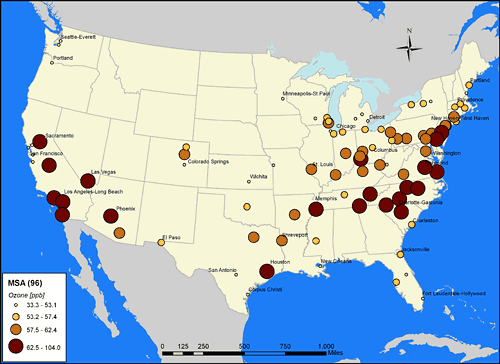
This map shows average ozone concentrations for the years 1977- 2000 in the 96 metropolitan regions included in a recent study of ozone-related health risks. The larger the circle, the higher the levels of ground-level ozone — the kind inhaled by humans. (Map courtesy of Bernie Beckerman, UC ) |
Long-term ozone exposure linked to higher risk of death
The gas, already implicated in global warming, is shown to have distinct impacts on human mortality
| 19 March 2009
BERKELEY — Long-term exposure to ground-level ozone, a major component of smog, is associated with an increased risk of death from respiratory ailments, according to a new nationwide study led by a Berkeley researcher.
The study, published in the March 12 issue of The New England Journal of Medicine, analyzes the risk of death associated with exposure to both ozone and fine particulate matter, two of the most prevalent components of air pollution. The study followed nearly 450,000 people for two decades and covered 96 metropolitan regions in the United States.
The researchers found that people living in areas with the highest concentrations of ozone, such as the Los Angeles metropolitan area and California's Central Valley, had a 25 to 30 percent greater annual risk of dying from respiratory diseases compared with people from regions with the lowest levels of the pollutant. Those locations included the Great Plains area and regions near San Francisco and Seattle.
"This is the first time we've been able to connect chronic exposure to ozone with the risk of death, arguably the most important outcome in health-impact studies used to justify air-quality regulations," says study lead author Michael Jerrett, associate professor of environmental-health sciences at Berkeley. "Previous research has connected short-term or acute ozone exposure to impaired lung function, aggravated asthma symptoms, increased emergency-room visits, and hospitalizations, but the impact of long-term exposure to ozone on mortality had not been pinned down until now."
The study found that for every 10 parts-per-billion (ppb) increase in ozone level, there is a 4 percent increase in risk of death from respiratory causes, primarily pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
"World Health Organization data indicate that about 240,000 people die each year from respiratory causes in the United States," says Jerrett. "Even a 4 percent increase can translate into thousands of excess deaths each year. Globally, some 7.7 million people die from respiratory causes, so worldwide the impact of ozone pollution could be very large."
The findings come a year after the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) strengthened its National Ambient Air Quality Standards for ground-level ozone from an annual average of 80 ppb to 75 ppb to reflect growing evidence of the harmful health effects of ozone. A group of leading scientists appointed to advise the EPA had actually recommended stricter health standards for ozone levels — from 60 to 70 ppb.
A month after the EPA released its new standards, a National Research Council report concluded that premature deaths related to ozone exposure of less than 24 hours are more likely among those with pre-existing diseases. The report called for more research on the link between mortality and ozone exposure over a period of weeks and years.
A matter of altitude
Ozone located in the upper atmosphere forms a protective layer against the sun's ultraviolet radiation. However, that same gas is toxic at ground level, where it can be breathed by humans. Ground-level ozone is formed through a complex chemical reaction in sunlight between nitrogen oxides (NOx), commonly spewed from vehicle exhaust, and industrial factory emissions.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change considers ground-level ozone, along with carbon dioxide and methane, to be one of the primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere.
"Ozone levels outdoors are not always highly correlated to ozone levels indoors, making it difficult to fully evaluate associations between ozone and health outcomes using ambient site monitors," says study co-author C. Arden Pope III, professor of economics at Brigham Young University. "The reality is that most of us spend the majority of our time indoors. But this study suggests that repeated exposures to elevated ozone levels over time have cumulative effects on respiratory health."
The new study analyzed data from 448,850 adults ages 30 and older, correlated with data from EPA air-pollution monitors while controlling for potentially confounding factors such as a participant's age, race, education, occupational exposures, smoking history, and diet.
Ozone data were obtained for the months of April and September between 1977 and 2000. Those months were chosen because ozone levels are typically higher when it's warmer and because insufficient data was available during the cooler months.
Researchers included EPA measurements of fine particulate matter — particles equal to or smaller than 2.5 micrometers in diameter and typically found in smoke and haze — when they became available in 1999 and 2000. Because fine-particle levels had already been linked to increased risk of premature death in previous studies, the researchers included them in the analysis to distinguish the effects of the two pollutants.
Over an 18-year follow-up period, 48,884 of the people in the study died from cardiovascular causes such as heart disease and strokes, and 9,891 died from respiratory causes.
As has been observed in previous studies, the researchers found that fine-particulate matter was linked to an increased risk of death from cardiovascular causes when analyzed alone and with ozone. The new finding was that the effects of ozone remained strongly linked to risk of death from respiratory problems even after fine-particle pollution was taken into account.
Not surprisingly, highly populated regions such as the Los Angeles, Riverside, and Houston areas, where the climate is sunny for much of the year and the air mass is relatively stable, had the highest average concentrations of ozone, ranging from 62.5 to 104 ppb. The regions with the lowest ozone levels had average concentrations of 33.3 to 53.1 ppb.
"Places like the Pacific North-west and the Minneapolis/St. Paul region are cooler and see more rain in the summer, which keeps the ozone levels in check," says Jerrett. "Similarly, the San Francisco Bay Area's infamous summertime fog blocks the sun and helps protect the region from high ozone levels."
Because ozone formation de-pends on a complex interaction of multiple factors, it is challenging to regulate, the study authors say. "Our study for the first time presents evidence suggesting that long-term exposure to ozone and fine-particle pollution have separate, independent effects on mortality, and that they seem to impact different parts of the body," says Jerrett. "We now know that controlling ozone is not only bene-ficial for mitigating global warming but could also have near-term benefits in the reduction of deaths from respiratory causes."

